The Vertigo Medication Trap: Why These Pills Are Making You Dizzy (Not Better) | Dr Prateek Porwal
🎯 TL;DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read)
Main trap: Vestibular suppressants (antihistamines, benzodiazepines, anticholinergics) provide SHORT-TERM relief but PREVENT the brain’s natural healing process (central compensation)
72-hour rule: Suppressants appropriate ONLY for first 24–72 hours of acute vertigo attack; beyond that, they delay recovery by months
BPPV reality: Physical repositioning maneuvers (Epley, Semont) cure 80–90% of cases; NO medication can move ear crystals back to normal position
Rebound dizziness: Abrupt medication withdrawal causes temporary severe dizziness, BUT this is a sign the brain is waking up—not disease recurrence
Safe exit: Gradual medication taper + early mobilization + vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) = true recovery (60–80% improvement)
Elderly risk: Suppressants dramatically increase fall risk, cognitive slowing, and drug-induced Parkinsonism in adults 65+
Action plan: If on dizziness pills >72 hours without diagnosis, ask for vestibular evaluation (Dix-Hallpike, HINTS) and supervised medication taper
Stop Calling Everything ‘Chakkar’: 3 Different Conditions That Mimic Each Other | PRIME ENT Center
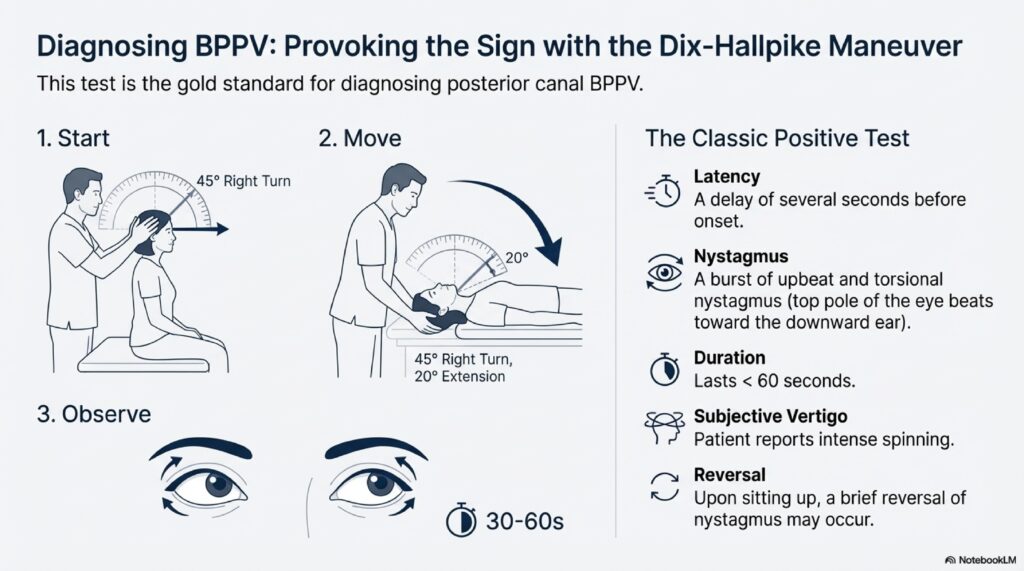
BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo): Seconds-long spinning triggered by specific head movements, caused by loose crystals in the inner ear. Treatable with Epley Maneuver (success rate 80-90%).
Vestibular Neuritis: Viral inflammation of the balance nerve causing persistent dizziness lasting hours to days. Self-limiting; recovery occurs with central compensation.
Posterior Circulation Stroke: Dangerous condition mimicking vestibular neuritis but identified by failing the HINTS exam (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew). Requires immediate emergency intervention.
Traveling with Vertigo? The 5-Minute Hack That Stops Motion Sickness Dead | Dr Prateek Porwal

The problem: Motion sickness = sensory mismatch (inner ear, eyes, body position disagree)—brain interprets as “toxin” → triggers vomiting center
The 5-minute hack: Daily vestibular habituation (gaze stabilization X1, head movement drills) for 3–7 days BEFORE travel = brain recalibrates
Immediate travel trick: Sit in front seat + fixate on horizon (aligns visual + vestibular signals) = prevents nausea
Critical medication rule: Vestibular suppressants (scopolamine, meclizine) = max 1–3 days ONLY (longer use = permanent dizziness)
Special conditions require prep: BPPV = morning exercises; migraine = 48-hour dietary restriction; Menière’s = sodium reduction; PPPD = visual desensitization
Pharmacological backup: Scopolamine patch (most effective), meclizine (less sedating), ondansetron (for breakthrough nausea)
Recovery goal: Teach brain to accept motion = habituation = sustained travel confidence without medication
Vertigo or Stroke? The 60-Second Test Every Patient Should Know | PRIME ENT Center Hardoi

TL;DR – Vertigo or Stroke: The HINTS Exam Explained Vertigo or stroke HINTS exam? The 60-second HINTS exam (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) is more accurate than MRI scans at detecting brainstem strokes. Key findings: Understanding this vertigo or stroke HINTS exam difference can be lifesaving in emergency situations. When to go to ER: […]
